Doubly Linked List Data Structure
Introduction to Doubly Linked List
A Doubly LinkedList is a variation of a linked list where the last node points back to the first node instead of null (or None in Python). This structure allows for a Doubly traversal where one can start from any node and eventually return to the same node. Doubly linked lists can be either singly or doubly linked.
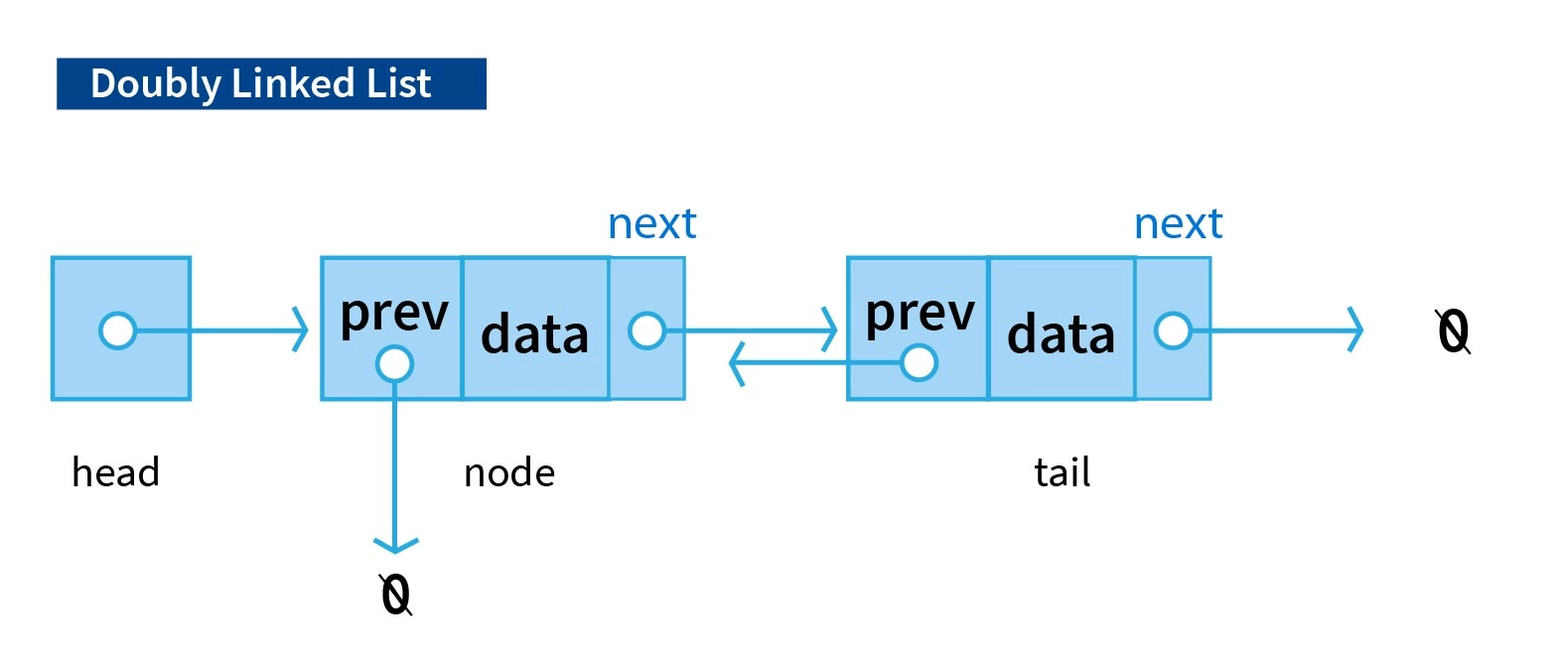
Doubly LinkedList Operations
A Doubly LinkedList typically supports the following operations:
- Insertion Operations : Insertion at the beginning or end involves adjusting the next pointers to maintain the Doubly nature, and potentially updating the head pointer.
- At the Beginning
- At the End
- After a Given Node
- Deletion Operations : Deletion of nodes, whether from the beginning, end, or a specific node, requires properly updating the references of adjacent nodes so that the Doubly structure is maintained.
- Delete from the Beginning
- Delete from the End
- Delete by Key
-
Search Operation : The search operation traverses the list until it either finds the required node or returns to the head.
-
Traversal Operation : Traversal begins from the head and continues until the node just before the head is encountered again.
Pseudocode
Basic Operations
-
Insert at the Beginning:
function insertAtBeginning(list : DoublyLinkedList, value : DataType) {
newNode = new Node(value)
if list.head is null {
list.head = newNode
list.tail = newNode
} else {
newNode.next = list.head
list.head.prev = newNode
list.head = newNode
}
} -
Insert at the End:
function insertAtEnd(list : DoublyLinkedList, value : DataType) {
newNode = new Node(value)
if list.tail is null {
list.head = newNode
list.tail = newNode
} else {
list.tail.next = newNode
newNode.prev = list.tail
list.tail = newNode
}
} -
Insert after a given node:
function insertAfter(list : DoublyLinkedList, node : Node, value : DataType) {
if node is null {
return // Invalid node
}
newNode = new Node(value)
newNode.next = node.next
newNode.prev = node
if node.next is not null {
node.next.prev = newNode
}
node.next = newNode
if node is list.tail {
list.tail = newNode // Update tail if necessary
}
} -
Delete a Node:
function deleteNode(list : DoublyLinkedList, node : Node) {
if node is null {
return // Invalid node
}
if node.prev is not null {
node.prev.next = node.next
} else {
list.head = node.next // Update head if it's the first node
}
if node.next is not null {
node.next.prev = node.prev
} else {
list.tail = node.prev // Update tail if it's the last node
}
// Optional: Clear the node to help with garbage collection
node = null
} -
Traverse Forward:
function traverseForward(list : DoublyLinkedList) {
current = list.head
while current is not null {
print(current.value)
current = current.next
}
} -
Traverse Backward
function traverseBackward(list : DoublyLinkedList) {
current = list.tail
while current is not null {
print(current.value)
current = current.prev
}
}
Implementation in Python, C++, and Java
Python Implementation
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insert_at_beginning(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.head
if self.head is not None:
self.head.prev = new_node
self.head = new_node
def insert_at_end(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
last = self.head
while last.next:
last = last.next
last.next = new_node
new_node.prev = last
def delete_node(self, key):
current = self.head
while current:
if current.data == key:
if current.prev:
current.prev.next = current.next
if current.next:
current.next.prev = current.prev
if current == self.head:
self.head = current.next
del current
return
current = current.next
print(f"Node with value {key} not found.")
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.data, end=" <=> ")
current = current.next
print("None")
# Example usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.insert_at_end(10)
dll.insert_at_end(20)
dll.insert_at_beginning(5)
dll.display() # Output: 5 <=> 10 <=> 20 <=> None
dll.delete_node(10)
dll.display() # Output: 5 <=> 20 <=> None
C++ Implementation
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node* prev;
Node(int data) {
this->data = data;
this->next = nullptr;
this->prev = nullptr;
}
};
class DoublyLinkedList {
public:
Node* head;
DoublyLinkedList() {
head = nullptr;
}
void insertAtBeginning(int data) {
Node* newNode = new Node(data);
newNode->next = head;
if (head != nullptr) {
head->prev = newNode;
}
head = newNode;
}
void insertAtEnd(int data) {
Node* newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == nullptr) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node* last = head;
while (last->next != nullptr) {
last = last->next;
}
last->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = last; e
}
void deleteNode(int key) {
Node* current = head;
while (current != nullptr) {
if (current->data == key) {
if (current->prev != nullptr) {
current->prev->next = current->next;
}
if (current->next != nullptr) {
current->next->prev = current->prev;
}
if (current == head) {
head = current->next;
}
delete current;
return;
}
current = current->next;
}
cout << "Node with value " << key << " not found." << endl;
}
void display() {
Node* current = head;
while (current != nullptr) {
cout << current->data << " <=> ";
current = current->next;
}
cout << "None" << endl;
}
};
// Example usage
int main() {
DoublyLinkedList dll;
dll.insertAtEnd(10);
dll.insertAtEnd(20);
dll.insertAtBeginning(5);
dll.display(); // Output: 5 <=> 10 <=> 20 <=> None
dll.deleteNode(10);
dll.display(); // Output: 5 <=> 20 <=> None
return 0;
}
Java Implementation
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
Node head;
public DoublyLinkedList() {
head = null;
}
public void insertAtBeginning(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
if (head != null) {
head.prev = newNode;
}
head = newNode;
}
public void insertAtEnd(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node last = head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
last.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = last;
}
public void deleteNode(int key) {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
if (current.data == key) {
if (current.prev != null) {
current.prev.next = current.next;
}
if (current.next != null) {
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
if (current == head) {
head = current.next;
}
return;
}
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("Node with value " + key + " not found.");
}
public void display() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " <=> ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("None");
}
}
// Example usage
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList dll = new DoublyLinkedList();
dll.insertAtEnd(10);
dll.insertAtEnd(20);
dll.insertAtBeginning(5);
dll.display(); // Output: 5 <=> 10 <=> 20 <=> None
dll.deleteNode(10);
dll.display(); // Output: 5 <=> 20 <=> None
}
}
Complexity
-
Time Complexity:
- Insertion :
- Deletion:
- Search:
- Traversal:
-
Space Complexity:
Conclusion
Doubly Linked Lists are powerful and versatile data structures that allow for efficient insertion and deletion from both ends and provides flexibility in traversing the list.